The seventeenth-century Italian painter Artemisia Gentileschi (1593–1654) was by far the most renowned woman artist of her era—and remains an icon of feminist art history. This exhibition sheds light on Gentileschi’s career in the Italian city of Naples, where she lived and worked beginning in 1630. Already a celebrated artist by the time she arrived in Naples, Gentileschi had established her reputation as a painter of powerful women—as exemplified by Bathsheba (about 1635–37), a masterful painting of the biblical heroine and a key work in CMA’s European collection.
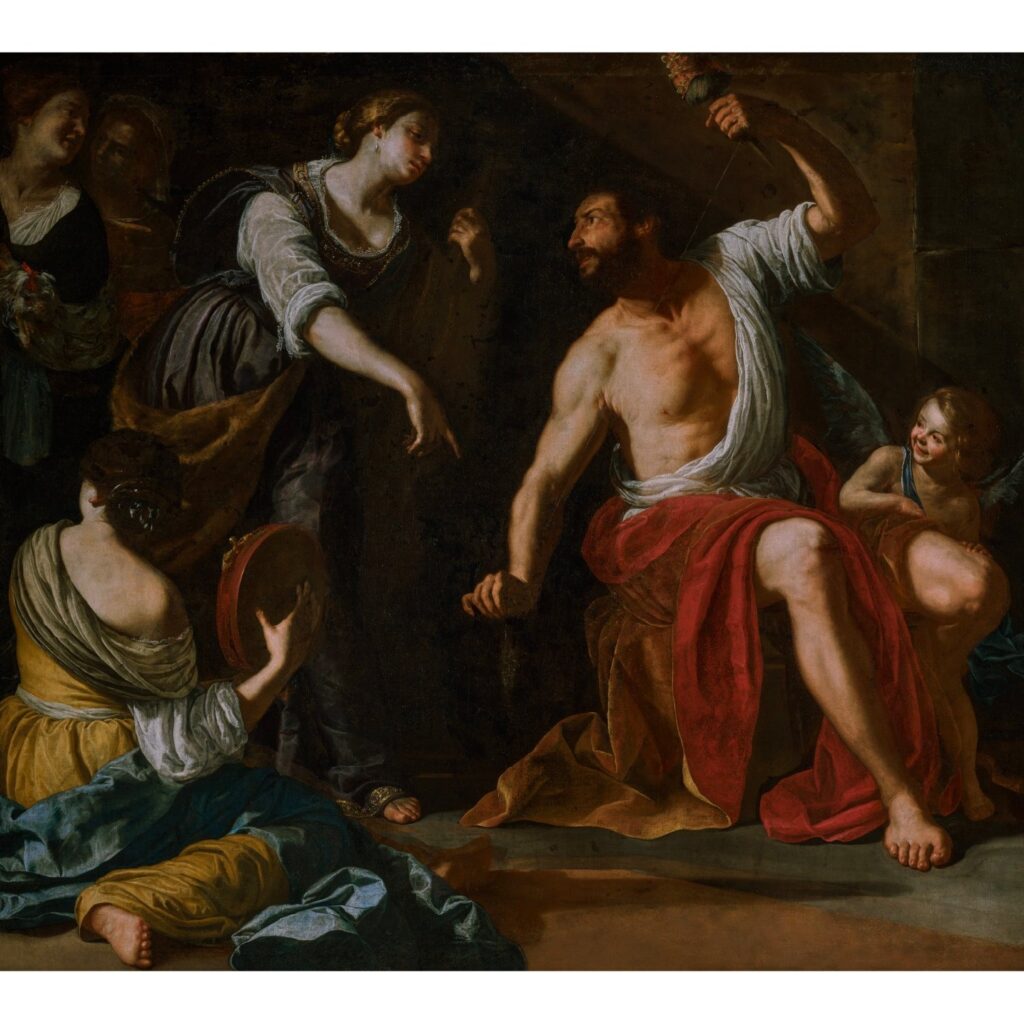
Artemisia Gentileschi: Naples to Beirut places Bathsheba in dialogue with another important work from the artist’s Neapolitan period, Hercules and Omphale (about 1635–37). This large-scale painting depicts a gender-bending episode from the myth of Hercules, in which the Greek hero is emasculated by his female captor Omphale, who forces him to wear women’s clothing and perform housework. Long considered lost, Hercules and Omphale resurfaced in Beirut, Lebanon, after a major explosion devastated much of the city on August 10, 2020. Damaged by the blast, the painting underwent a lengthy process of conservation at the Getty Museum in Los Angeles before appearing on view in public for the first time in June 2025.
Hercules and Omphale anchors an intimate selection of paintings by the artist and her contemporaries, including Artemisia’s Lucretia (about 1627), which was recently acquired by the Getty. The exhibition offers a behind-the-scenes view of the Getty’s conservation of Hercules and Omphale, while also exploring the wider history of its mythological subject. As a tribute to the painting’s city of origin, Naples to Beirut also features a wall installation by Lebanese artist and art historian Gregory Buchakjian, whose identification of Hercules and Omphale in the aftermath of the 2020 explosion has brought this remarkable work to light—now fully restored.
slide 2 of 4



 Tue, Jan 13 • All Day
Tue, Jan 13 • All Day Burgers
Burgers Deli-Sandwiches
Deli-Sandwiches Cafe-Coffee
Cafe-Coffee Mexican
Mexican Pizza
Pizza Italian
Italian Middle Eastern
Middle Eastern Wine Bar
Wine Bar Bakery
Bakery Beer Bar/Hall
Beer Bar/Hall